The AI Capability Framework: Six Levels of AI Power and Automation
How to Level up You AI Output
AI tools are transforming from simple question-answering machines into sophisticated, autonomous digital partners. But to understand this evolution, it’s useful to look at specific criteria that mark an AI’s functionality across different levels. In this article, we’ll explore these key criteria, showing how they apply to AI assistants in general.
Levels of AI Sophistication (Automation and Power)
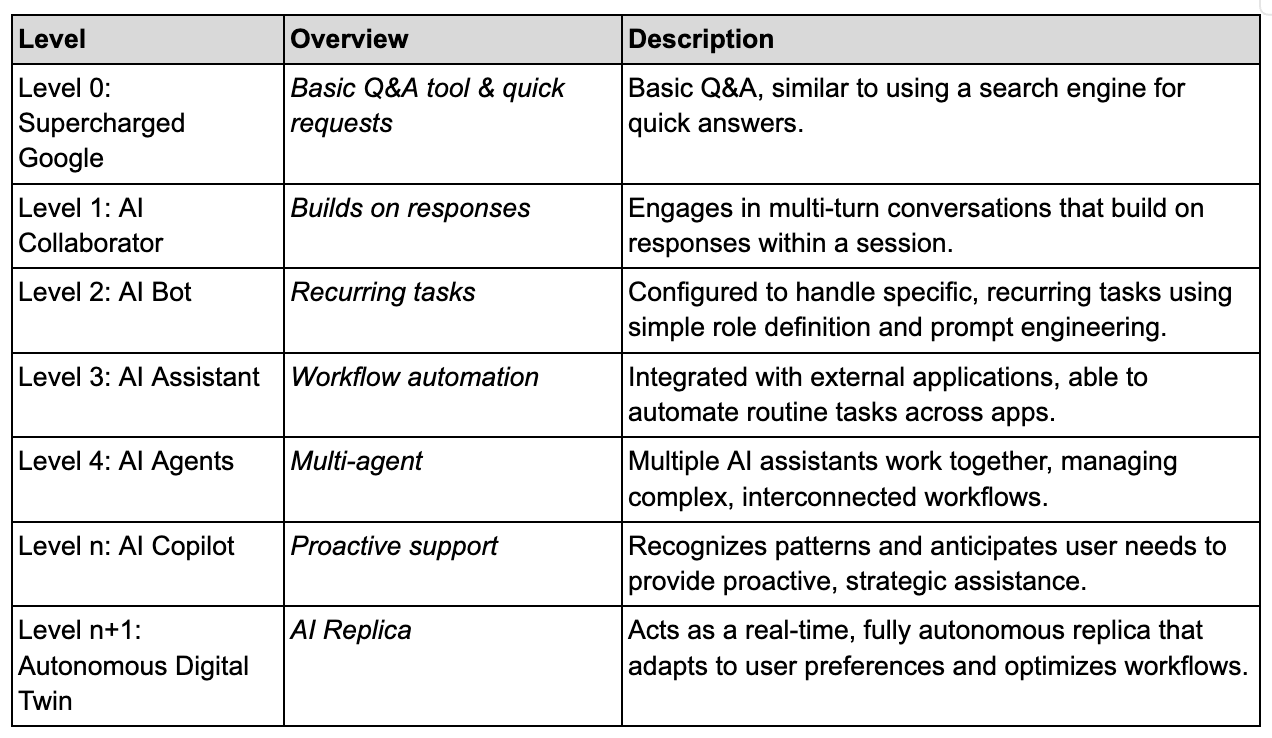
We identified various levels from Level 0 (Supercharged Google) to Level n+1 (Autonomous Digital Twin), demonstrating how AI assistants transform from basic information retrieval tools into adaptive, proactive digital partners that autonomously manage complex workflows.
As the levels progress, AI’s ability to handle tasks autonomously and within specific roles evolves significantly, from simple Q&A to fully autonomous assistance.
As the levels progress, AI’s ability to handle tasks autonomously and within specific roles evolves significantly, from simple Q&A to fully autonomous assistance.
The Levels Explained
Most of us play at Level 0 or 1.
Criteria of AI Sophistication
ChatGPT serves as an example of an AI assistant, helping illustrate these features and levels of functionality.
The criteria are as follows:
Initial Setup, Development, and Training – Describes the setup required to define an AI’s roles, workflows, and prompts.
Automation, Integration, and Workflow Support – Explores the AI’s ability to support structured workflows, integrate with external tools, and automate tasks.
Inter-AI and System Integration – Reflects the AI’s capacity to work with other AI agents and systems for comprehensive support.
Proactive Assistance and Anticipation – Indicates the AI’s capability to provide proactive recommendations and anticipate needs.
Decision Simulation and Outcome Prediction – Reflects the AI’s capacity to simulate outcomes or scenarios for decision-making.
Each criterion helps define an AI assistant’s role at each level, from reactive assistance to a proactive, autonomous digital partner. Below, we’ll break down how each criterion applies across levels, from Level 0 (simple search engine-type functions) to Level n+1 (Autonomous Digital Twin).
Let’s dig in.
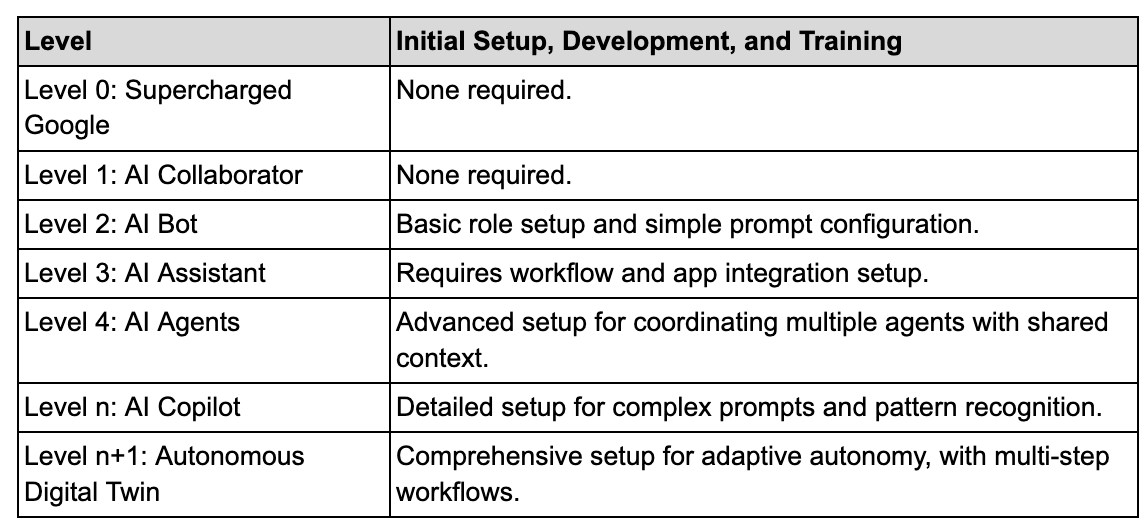
1. Initial Setup, Development, and Training
This criterion describes the level of setup needed to define an AI’s roles, workflows, and prompts. Starting with no setup at Level 0, the requirement grows as the levels advance, with extensive setup needed at higher levels for advanced, autonomous function.
Using ChatGPT as an example, at Level 0, it functions as a Q&A tool, requiring no setup from the user. As it advances, more sophisticated configurations allow ChatGPT to take on specific roles or handle workflows independently, eventually culminating in a comprehensive setup where the AI learns the user’s style, preferences, and tasks to operate autonomously.
2. Automation, Integration, and Workflow Support
This criterion combines the AI’s ability to support structured workflows, connect with other applications, and automate tasks. Higher levels enable more complex workflows, allowing the AI to automate end-to-end processes.
ChatGPT illustrates this progression well. At Level 0, it has no automation capacity, providing only simple answers. As it advances to Level 3, it gains the ability to connect with apps like calendars and project management tools, helping automate basic workflows. By Level n+1, it operates independently, handling complex, multi-step tasks with full end-to-end automation.
3. Inter-AI and System Integration
This criterion describes the ability of the AI to work across multiple AI assistants and integrate with other systems, coordinating on complex workflows and sharing data seamlessly. Higher levels facilitate smooth interaction between various agents and systems.
For instance, in its advanced stages, ChatGPT can operate as part of an integrated system, coordinating with other AI tools (e.g., a scheduling bot or content generation assistant) to manage interconnected workflows and streamline tasks.
4. Proactive Assistance and Anticipation
At higher levels, the AI can analyse patterns and provide proactive suggestions, anticipating user needs. Lower levels don’t offer any proactive support, but this capability becomes progressively more advanced at higher levels.
Using ChatGPT as an example, lower levels may respond to commands or questions but cannot proactively offer insights. At advanced levels, it begins recognising patterns in tasks, providing useful suggestions based on prior interactions.
5. Decision Simulation and Outcome Prediction
This criterion highlights the AI’s ability to simulate outcomes and predict the results of decisions, a powerful capability useful for complex decision-making and strategic planning.
At its most advanced levels, ChatGPT serves as an example of how an AI assistant can move beyond reactive tasks to simulate different outcomes. For instance, it could simulate project risks or model possible outcomes for strategic choices.
Conclusion
Understanding the criteria for AI functionality, from initial setup and training to decision simulation, provides insight into the progression from basic question-answering tools to advanced, autonomous digital partners. Each level marks an increase in capabilities, with higher levels requiring more setup and offering more complex automation, integration, and proactive assistance.